How IV Therapy for Iron Deficiency Supports Recovery From Anemia

Medically reviewed by Micaela Strevay, FNP-C, PMHNP-BC
Joseph Lopez • September 27, 2025
Table of Contents
Iron deficiency is one of the most common causes of anemia worldwide. It happens when your body lacks enough iron to produce hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells. Without hemoglobin, your organs and tissues receive less oxygen, making you feel weak and tired.
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when low iron levels reduce the number of healthy red blood cells. This condition is sometimes called iron-poor blood, since oxygen delivery to tissues is reduced. This leads to a variety of symptoms, such as:
- Constant fatigue and weakness–You may feel drained even after resting, as muscles and organs don’t receive enough oxygen.
- Pale or yellowish skin–Reduced red blood cells change skin tone, often making lips and nails look lighter too.
- Shortness of breath, even with mild activity–Simple tasks like climbing stairs or walking may leave you winded.
- Frequent headaches or dizziness–The brain is highly sensitive to low oxygen, causing pressure or lightheadedness.
- Reduced concentration and focus–Iron deficiency anemia makes it harder to stay alert, affecting work and daily tasks.
These symptoms greatly impact daily life. Tasks feel harder, energy levels drop, and recovery after activity slows. For many, it also reduces work productivity and overall quality of life. That’s why early diagnosis of iron deficiency, usually confirmed with a complete blood count (CBC) and iron studies, is essential.
Why Oral Iron Isn’t Always Enough
Doctors usually recommend iron supplement pills as the first treatment for anemia. However, not every patient responds well to them. Some people absorb iron poorly because of gastrointestinal diseases like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or chronic gastritis. In these cases, the body cannot absorb enough iron from food or pills, no matter the dose.
Others stop taking them because of the side effects of iron supplements. Common issues include:
- Constipation or stomach pain–Iron irritates the digestive tract in some people.
- Nausea or vomiting–Especially when taken on an empty stomach.
- Dark stools or indigestion–These can make long-term use uncomfortable.
Even when tolerated, oral iron is slow. It may take several months to restore normal hemoglobin levels. During this time, fatigue, weakness, and other symptoms continue or even worsen.
This delay is especially concerning for people with severe anemia, pregnant women, or those with ongoing blood loss. For them, waiting too long can put additional stress on the heart and raise the risk of high blood pressure or fatigue-related complications.
This is why doctors often recommend intravenous iron infusion as part of the management of iron deficiency anemia.
How IV Therapy Works for Iron Deficiency
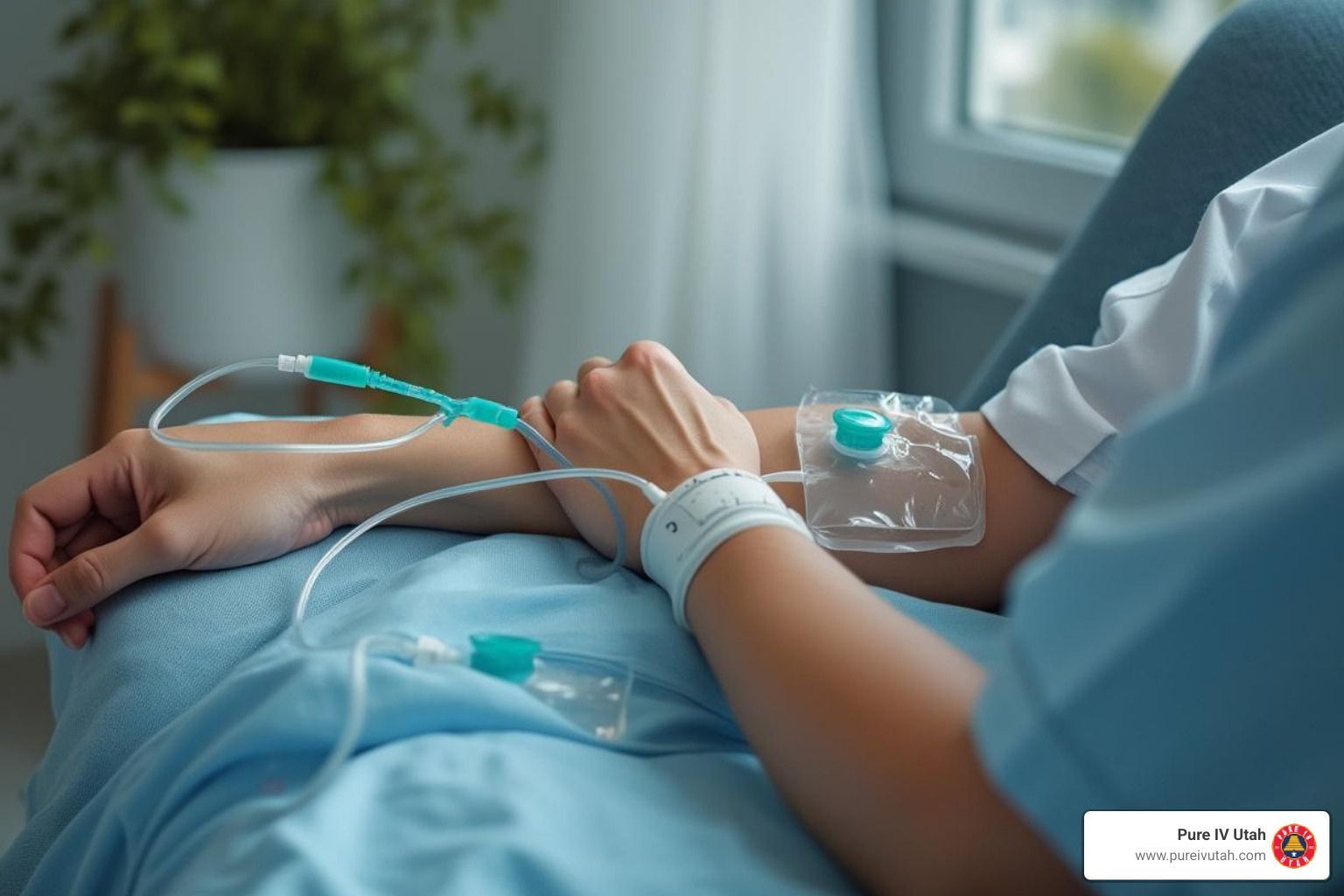
IV iron therapy delivers iron directly into your bloodstream through an intravenous infusion. By bypassing the digestive system, your body absorbs nearly the full intended dose without loss. This makes the treatment more effective than oral iron formulations.
The process is straightforward and carefully monitored:
- A healthcare professional inserts a small IV line into a vein, usually in the arm.
- The iron solution is infused slowly to minimize reactions.
- The session can last anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the iron formulations used and dosage.
- Several intravenous iron sessions may be required to restore healthy iron saturation levels.
Providers often monitor your heart rate, blood pressure, and comfort during the infusion. Blood tests, including iron saturation and a complete blood count, help track recovery.
Because of its speed and efficiency, IV iron therapy is often recommended when:
- Oral iron supplement pills don’t work or cause intolerable side effects.
- Anemia is severe and needs quick correction.
- Patients require faster recovery before surgery, pregnancy, or a blood disorder demands a quick recovery.
For many, IV iron infusions not only restore iron faster but also improve energy, concentration, and quality of life within weeks rather than months.
Benefits of Intravenous Iron Therapy for Anemia Recovery
Intravenous iron offers several advantages compared to oral supplements, especially for people with moderate to severe anemia.
- Rapid improvement in iron levels–Unlike oral iron supplements that take months, IV iron infusion therapy raises iron and hemoglobin much faster. Many patients notice improvements in energy and well-being within days to weeks after treatment.
- Faster relief from symptoms–Common complaints like fatigue, dizziness, headaches, and weakness improve more quickly with iron infusion. With more oxygen reaching tissues, daily tasks such as walking, working, or exercising become easier again.
- Fewer digestive issues–Because IV iron bypasses the stomach, it avoids common side effects of oral iron. Patients who struggle with nausea, constipation, or abdominal pain from pills often tolerate IV iron infusions better.
- Better absorption–The body receives the full dose directly into the bloodstream. This is particularly beneficial for people with digestive conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or chronic gastritis, where oral absorption is poor.
- Improved daily functioning–Restored iron levels bring back mental clarity, physical energy, and emotional balance.
- Support during special circumstances–IV iron is often recommended in pregnancy, pre-surgical patients, or those with ongoing blood loss. It ensures the body recovers faster and avoids complications linked to severe anemia.
For many, this treatment of iron deficiency means a faster return to normal life. This also improves health outcomes and reduces the stress and frustration of living with long-term symptoms.
Who May Need Intravenous Iron for Iron Deficiency
Not everyone with anemia requires IV iron therapy. Some can recover with diet changes or oral supplements. However, iron infusion therapy is especially helpful for certain groups:
- People with severe iron deficiency anemia and low hemoglobin levels–When iron stores are dangerously low, oral iron supplements are often too slow. Iron infusion therapy raises hemoglobin faster, helping prevent complications like heart strain or fainting.
- Patients who cannot tolerate oral supplements–Many people stop taking iron pills because of stomach pain, constipation, or nausea. Intravenous iron avoids these side effects and provides a more comfortable way to restore iron levels.
- Individuals with inflammatory bowel disease or other gastrointestinal conditions–Diseases like Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis, or celiac disease interfere with nutrient absorption. In these cases, oral iron supplements pass through the digestive system without being absorbed. Intravenous iron therapy ensures the body receives and uses the iron effectively.
- Pregnant women with significant iron deficiency–Pregnancy increases iron needs for both mother and baby. If oral iron supplementation isn’t enough, intravenous iron may be prescribed under close supervision to prevent complications like preterm birth or low birth weight.
- Patients with ongoing blood loss–Heavy menstrual bleeding, blood disorders, ulcers, or chronic conditions such as kidney disease can cause constant iron loss. Iron infusion therapy helps replace what the body cannot keep up with through diet alone.
Doctors typically confirm the need for IV iron infusions through blood tests and medical history. The decision is individualized to ensure safety and effectiveness for each patient.
Possible Risks and Side Effects
IV iron therapy is generally safe, especially when administered by licensed professionals in a clinical setting. Most side effects, if they occur, are mild and short-lived. These may include:
- Injection site discomfort–Temporary pain, swelling, or bruising where the IV is placed.
- Mild headache, dizziness, or nausea–Usually resolves within a few hours.
- Muscle cramps or metallic taste–A common but brief reaction during iron infusion.
In rare cases, more serious side effects can occur:
- Allergic reactions–Some patients may experience rashes, itching, or, rarely, breathing problems.
- Low blood pressure–A sudden drop may happen during iron infusion, but providers monitor and manage it quickly.
- Iron toxicity–Iron overload can strain the heart, liver, or brain. Too much brain iron has been linked to neurological problems, highlighting the need for proper dosing.
With proper screening, dosing, and medical supervision, the chances of serious complications are very low. Most patients complete intravenous iron infusion safely and experience significant improvement in their anemia symptoms soon after treatment.
Maximizing Recovery With Intravenous Iron Therapy
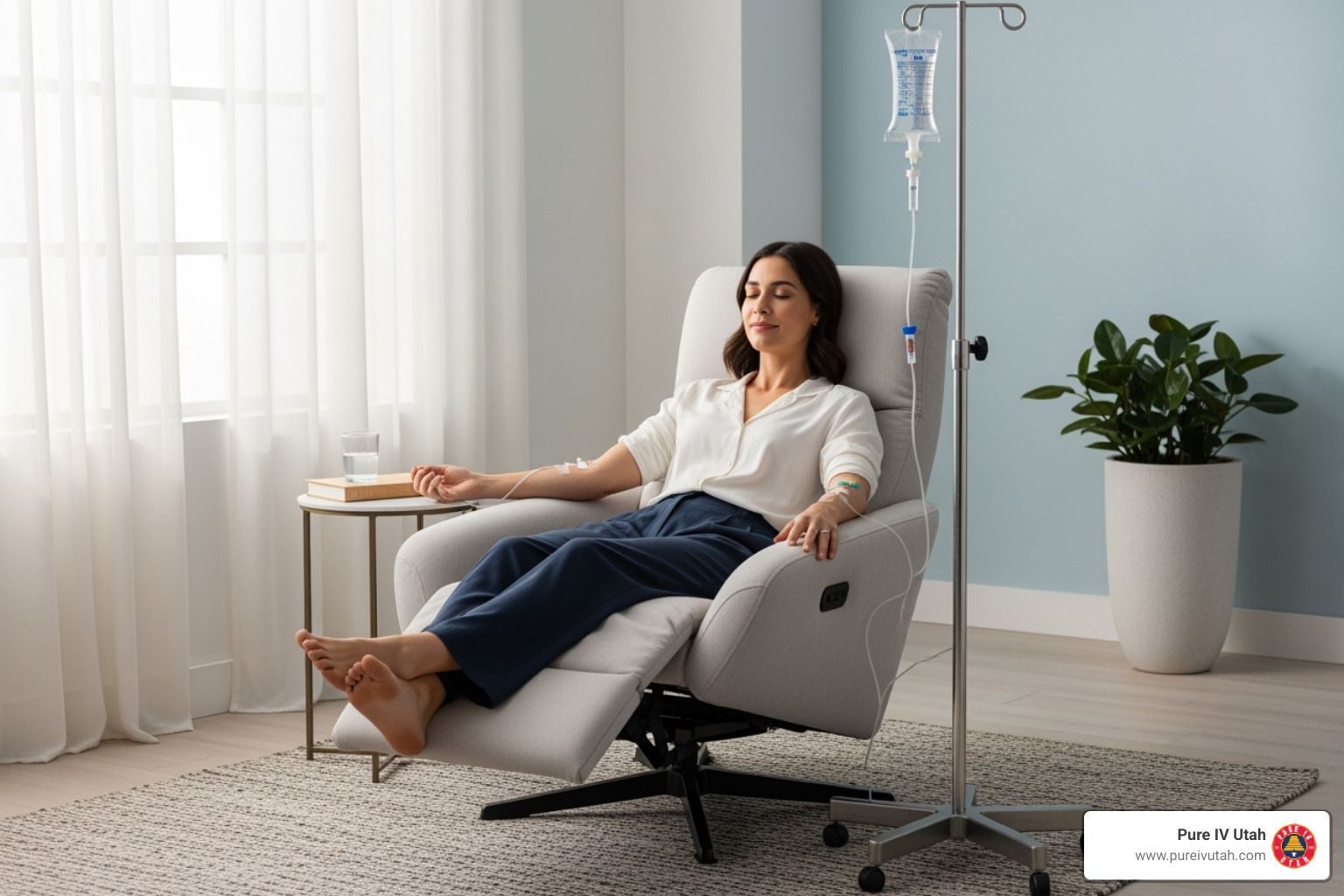

IV iron therapy can quickly restore iron levels, but lasting recovery depends on more than IV iron alone. To get the best results, combine treatment with ongoing monitoring and healthy habits that keep your iron stores stable.
Here are key steps to maximize recovery:
- Follow medical guidance–Regular blood tests help track hemoglobin, iron toxicity, and ferritin levels, ensuring safe and effective treatment.
- Eat iron-rich foods–Include lean red meat, beans, lentils, spinach, and fortified cereals in your meals.
- Pair with vitamin C–Foods like oranges, bell peppers, and strawberries improve how well your body absorbs iron.
- Avoid absorption blockers–Limit tea, coffee, and high-calcium foods around iron-rich meals.
- Address underlying causes–Manage heavy periods, digestive issues, or other blood disorders.
- Support overall health–Prioritize sleep, hydration, and moderate activity to boost energy and recovery.
When combined with medical supervision, intravenous iron therapy is one of the safest and most effective options for the treatment of iron deficiency. It allows patients to regain strength, energy, and confidence in their daily lives.
While medical IV iron infusions are mostly done in clinical settings, wellness IV therapy can also support recovery and overall energy. Pure IV Utah offers personalized IV drips designed to boost hydration, energy, and immunity. This can complement your long-term health goals.